Introduction to Foundry Moulding Sands
Foundry moulding sands are a critical component in the metal casting process, serving as the material in which the mold cavity is formed. The quality and characteristics of these sands directly impact the quality of the cast products.
Types of Foundry Moulding Sands
- Natural Moulding Sands
- Occurrence and Characteristics: Natural moulding sands contain appreciable amounts of clay, which acts as a bond between sand grains. These sands possess varying levels of strength, plasticity, and refractoriness depending on the clay minerals present. They are often processed by crushing and milling to achieve the desired distribution of clay particles around the sand grains.
- Common Types in India: Principal natural moulding sands include Damodar and Barakar sands (Bengal-Bihar border), Oyaria sand (Bihar), Batala sand (Punjab), Bhavnagar sand (Saurashtra), and others. These sands are widely used in iron and non-ferrous foundry practices due to their economic advantages and local availability.
- Bank Sands Including Dune Sands
- Characteristics and Usage: These sands have low clay content and are sourced from river beds, sea coasts, and dunes. They are mainly used for blending with natural moulding sands to enhance permeability and reduce the strength of the sand mixtures, making them suitable for core making.
- High Silica Sands
- Properties and Sources: High silica sands are predominantly composed of quartz and have minimal clay content. They are characterized by high refractoriness, making them ideal for steel foundry practices. Major sources include Rajmahal sand (Bihar), Jamshedpur sand, and Allahabad sand. These sands may require washing and grading to ensure they meet the specific needs of foundries.
- Special Sands
- Types and Applications: Special sands such as zircon, sillimanite, and olivine are used for high melting point alloy castings. These sands have unique properties like low linear expansion and high thermal conductivity, making them suitable for specialized casting processes. For instance, zircon sand from Quilon (Kerala) is known for its chemical inertness and high refractoriness.
- Synthetic Sands
- Composition and Advantages: Synthetic sand mixtures are prepared by bonding high silica sand with clays like bentonite. These mixtures allow for precise control over the sand properties, making them ideal for mechanized foundries. Synthetic sands are preferred in modern foundries due to their consistent quality and performance.
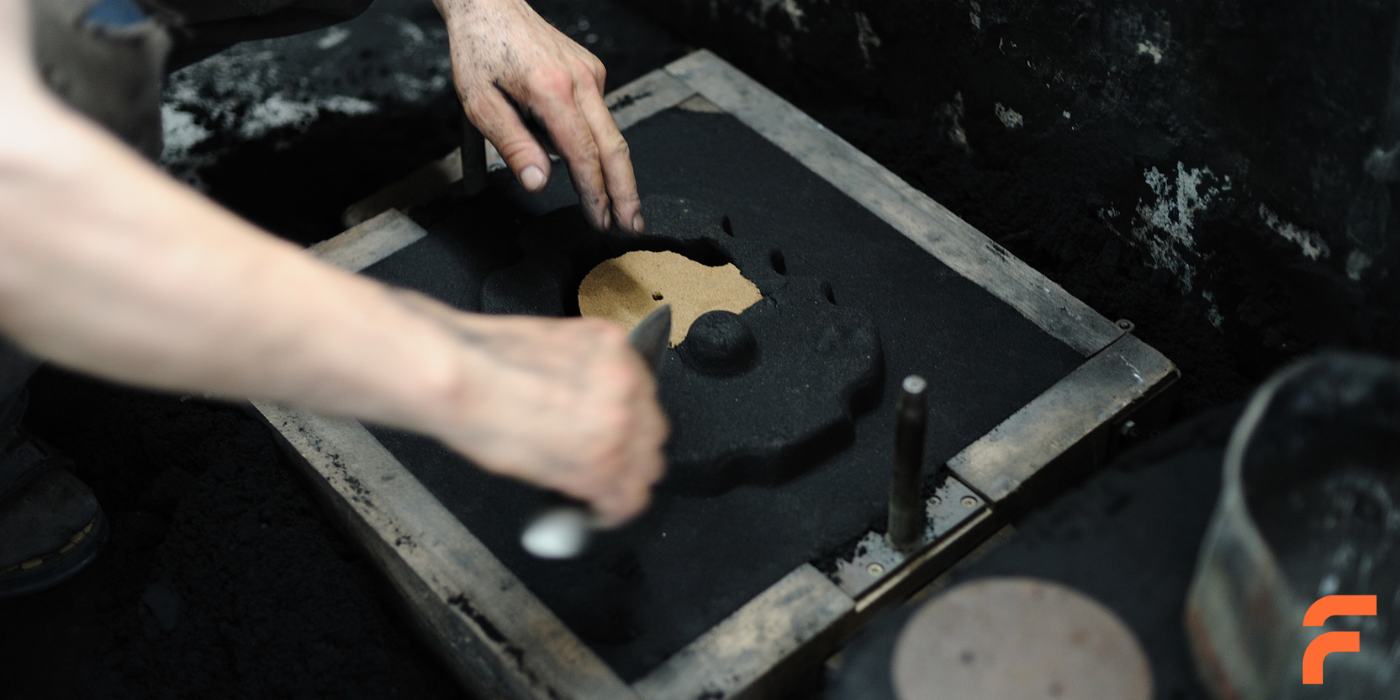

Properties of Foundry Moulding Sands
The quality of a moulding sand is determined by several properties:
- Refractoriness: The ability to withstand high temperatures without melting or breaking down.
- Plasticity: The ability to be shaped and retain the shape.
- Strength: The capacity to withstand the forces during the casting process.
- Permeability: The ability to allow gases to escape through the sand.
- Durability: The longevity of the sand under repeated use.
- Flowability: The ease with which the sand fills the mold.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of foundry moulding sands and their properties is crucial for optimizing the casting process and ensuring high-quality cast products. By selecting the appropriate sand type and composition, foundries can achieve better performance, reduce defects, and enhance the overall efficiency of their operations.