As of February 2024, India is the world’s second-largest producer of castings, with an annual production of 12 million tons.
The foundry industry is the mother of all industries. The Indian foundry industry has long been a key contributor to the country’s manufacturing sector.
1. Latest statistics of Indian Foundry Industry in 2024
The Indian foundry industry continues to grow steadily, driven by increasing demand in domestic and international markets. In 2023, India produced over 12 million tonnes of castings, marking a 5% increase compared to the previous year. The country now ranks as the second-largest casting producer globally, behind China. With more than 4,500 foundries operating across India, the industry employs over 500,000 people directly and indirectly.
“In 2024, India’s foundry sector is expected to grow further, with projections estimating a 7% increase in output, driven by rising global demand and advancements in production technologies.”
2. Government Policies and Initiatives
The Indian government has recognized the foundry industry’s importance and continues to implement supportive policies through initiatives like ‘Make in India’ and Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes. These policies aim to boost local manufacturing, reduce import dependency, and increase exports.
In 2024, the government introduced additional tax benefits and subsidies for foundries adopting clean energy and digitalization practices, encouraging the sector to modernize and become more competitive in the global market.
“Government initiatives are paving the way for the modernization of India’s foundries, encouraging them to adopt energy-efficient technologies and digitalization for improved productivity.”
3. Technological Advancements and Sustainability Efforts
Indian foundries are increasingly adopting advanced technologies like automation, Industry 4.0, and green foundry practices to stay competitive. These advancements include the use of smart sensors, robotics, and AI-driven systems that improve production efficiency and reduce wastage.
Sustainability is also becoming a priority, with more foundries adopting eco-friendly processes such as waste heat recovery systems, low-emission melting techniques, and recycling of sand and other materials.
“The rise of green foundries in India is a testament to the industry’s commitment to sustainability. This shift not only reduces the environmental impact but also opens doors to international markets that demand eco-friendly products.”
4. Challenges Facing the Indian Foundry Industry
Despite its growth, the Indian foundry industry faces several challenges. Rising raw material costs, particularly for iron and steel, have increased production expenses. Additionally, fluctuations in global trade relations have led to unpredictable export markets, impacting the industry’s stability.
Another challenge is the skilled labor shortage. As the industry modernizes, the demand for workers proficient in operating advanced machinery and digital systems grows, and there is a gap in training programs to meet this demand.
“Addressing these challenges will require a combination of government support, industry-wide collaboration, and investment in training and development for the workforce.”
5. Opportunities: Electric Vehicles and Lightweight Castings
One of the most promising opportunities for the Indian foundry industry lies in the electric vehicle (EV) market. As global demand for EVs rises, the need for lightweight materials like aluminum and magnesium castings becomes crucial. Indian foundries are well-positioned to capitalize on this trend, particularly in producing lightweight chassis components and battery housing.
“The growing EV market offers Indian foundries a chance to diversify and specialize in lightweight casting production, creating new export opportunities to regions like Europe and North America.”
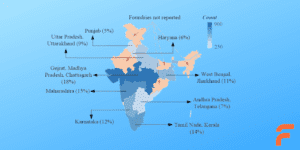
6. Regional Hubs: Coimbatore and Gujarat Leading the Way
India’s foundry production is concentrated in key regions, with Coimbatore and Gujarat standing out as major hubs. Coimbatore alone accounts for nearly 40% of the country’s total casting output, producing high-quality components for automotive, pump, and valve industries.
Gujarat, with its strategic location and well-developed infrastructure, has become a preferred destination for large-scale foundries, especially those focused on exports.
“Coimbatore and Gujarat continue to lead India’s foundry industry, thanks to their strong infrastructure, skilled labor force, and proximity to key markets.”
7. India’s Position in the Global Market
India’s position in the global foundry market is solid, with a significant share of its castings exported to countries across Europe, North America, and the Middle East. However, the industry faces stiff competition from China and Turkey, which offer competitive pricing and higher production capacity.
To remain competitive, Indian foundries must innovate, adopt sustainable practices, and improve operational efficiency.
“By embracing technological advancements and sustainability, Indian foundries can strengthen their position in the global market and tap into emerging opportunities like electric vehicles and renewable energy infrastructure.”
Conclusion: A Bright Future for Indian Foundries
The future of India’s foundry industry looks bright, with growth projected in both domestic and international markets. While challenges like rising material costs and labor shortages persist, the opportunities presented by new technologies, government support, and expanding sectors like electric vehicles provide hope for continued progress.
By staying at the forefront of innovation and sustainability, India’s foundries can not only retain their place as global leaders but also set new benchmarks for efficiency and environmental responsibility.





