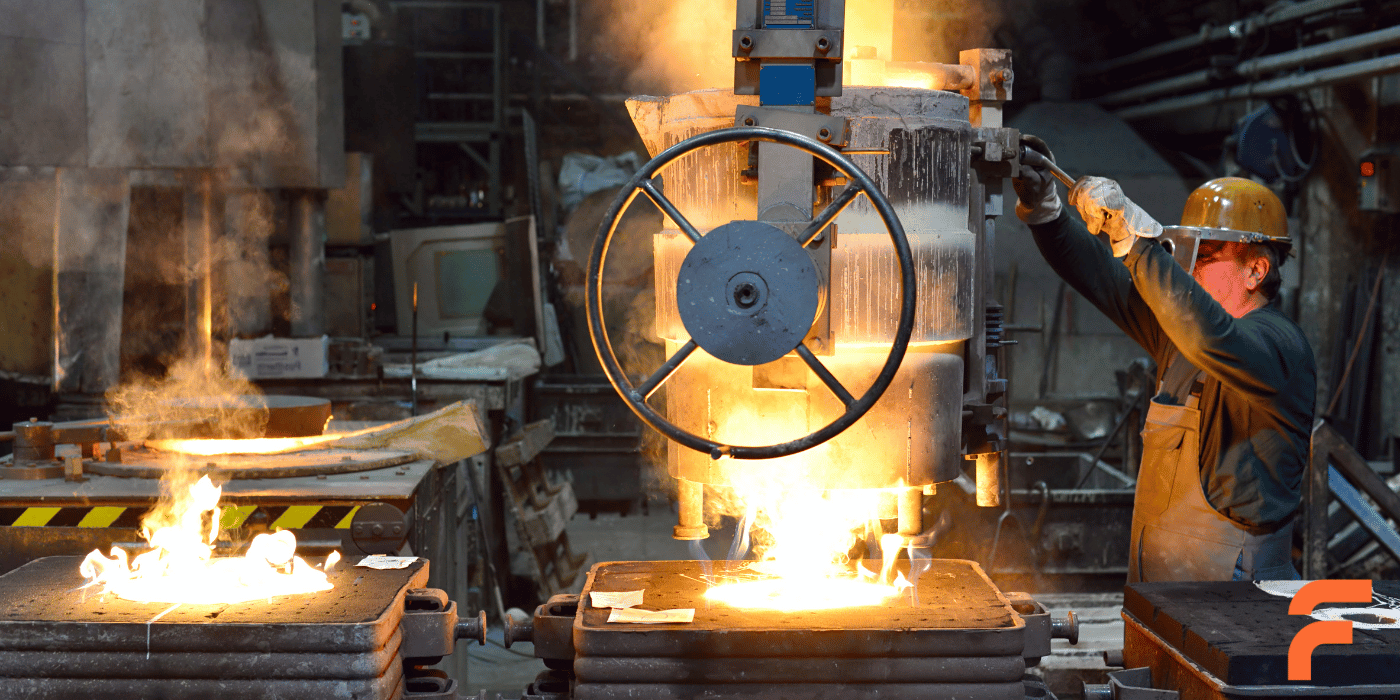
Investment casting is a transformative process in the foundry industry, renowned for its precision and ability to produce complex metal components.
Understanding the Investment Casting Process
Investment casting, or lost-wax casting, is a method that creates intricate shapes by forming a mold around a wax model. This technique is particularly favored for high-precision applications across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Investment Casting Process:
-
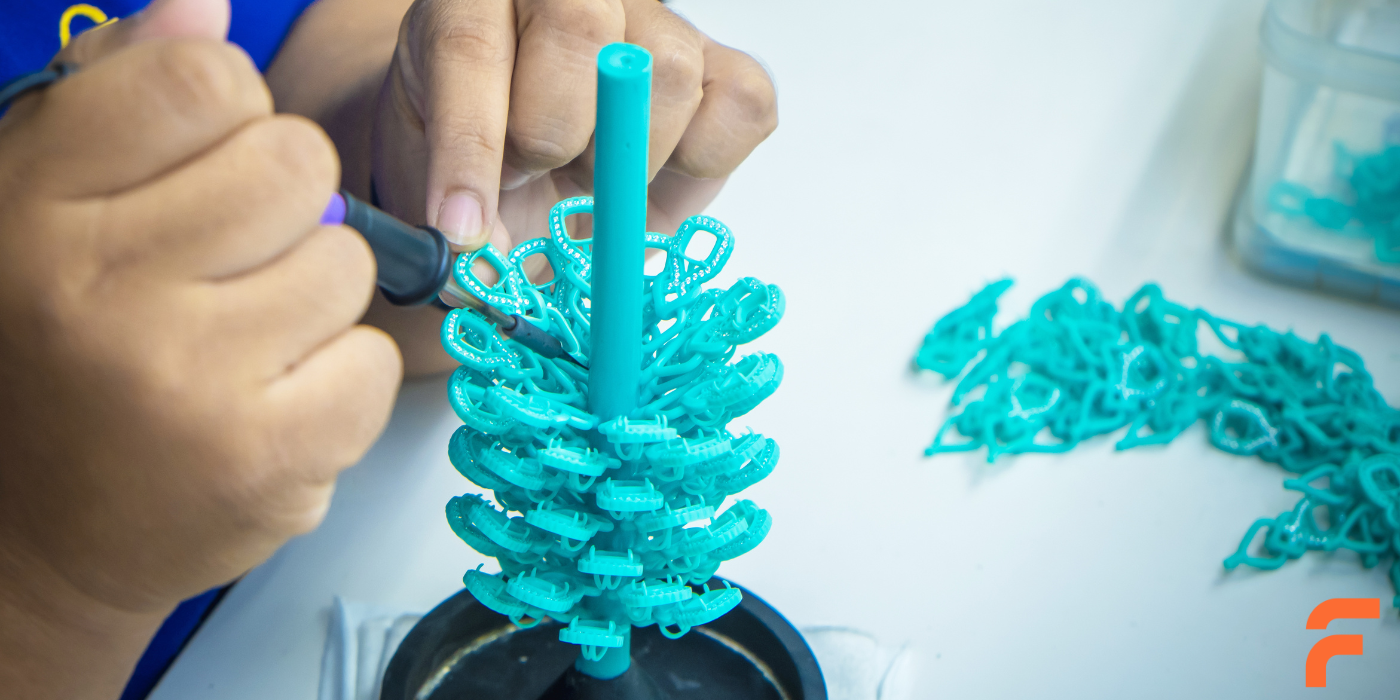
Pattern Creation
The journey begins with crafting a wax pattern that replicates the final part. These patterns are designed with precision, considering shrinkage during the cooling process to maintain dimensional accuracy.

-
Shell Building
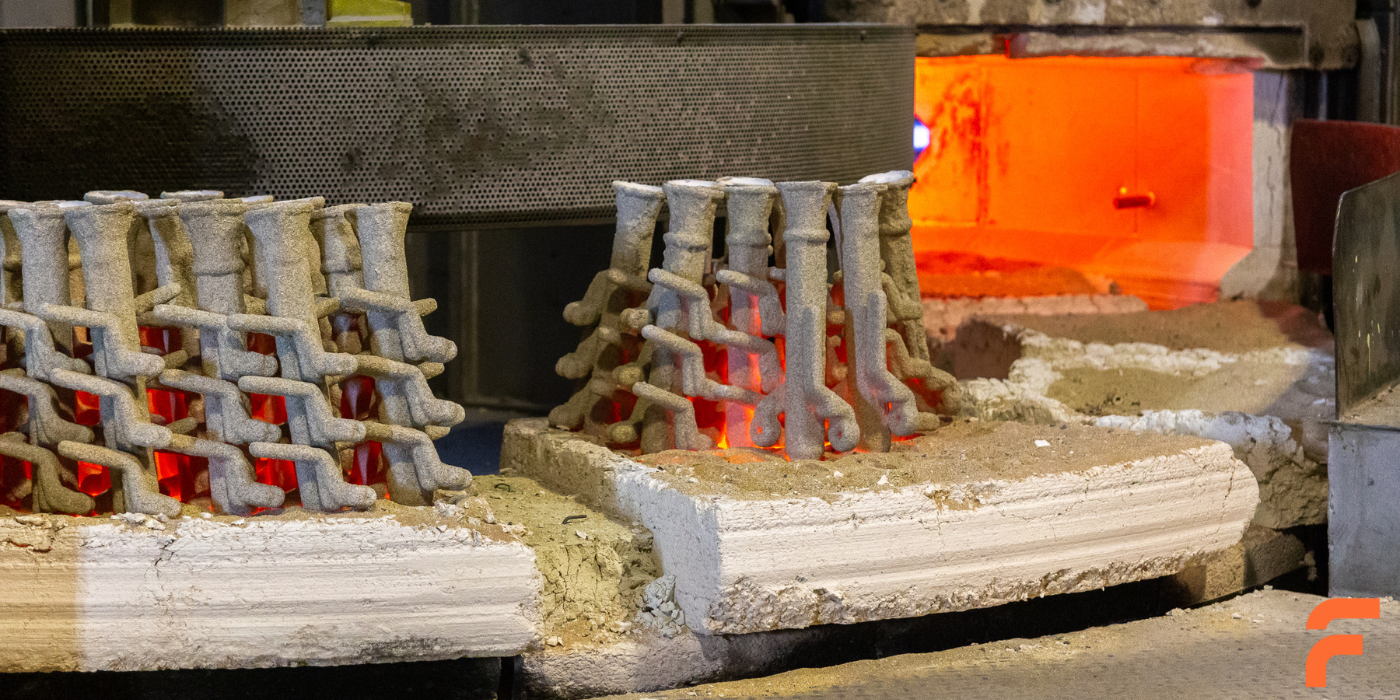
Once the wax pattern is ready, it is coated with a ceramic material to form a strong shell. This shell must withstand the high temperatures of molten metal while retaining its shape.
-
Wax Removal
After the shell hardens, the next step involves melting away the wax pattern, creating a cavity for the molten metal. This is often done through heating, ensuring the shell remains intact.
-
Pouring
Metal is melted in a furnace and poured into the cavity created by the wax model. Careful pouring is essential to avoid defects and ensure the mold fills.
-
Cooling and Solidification
Once poured, the molten metal cools and solidifies within the mold. Managing the cooling rate is crucial to prevent issues such as porosity or cracking.
-
Shell Removal
After the metal has solidified, the ceramic shell is broken away to reveal the cast part. This step may involve various methods, including vibration or water jetting.
-
Finishing and Inspection
The final part undergoes finishing processes like machining, grinding, and surface treatment to achieve the desired surface quality. Thorough inspection ensures that each component meets stringent specifications, often utilizing non-destructive testing methods.
Advantages of Investment Casting
Precision and Complexity: Investment casting excels at producing parts with intricate geometries and tight tolerances that traditional methods struggle to achieve.
Excellent Surface Finish: The process results in a smooth finish, minimizing the need for extensive post-processing.
Material Versatility: A wide range of materials, including various alloys and high-performance metals, can be utilized, offering manufacturers flexibility in material selection.
High-Dimensional Accuracy: Investment casting provides exceptional accuracy, which is vital for components requiring precise fit and functionality.
Reduced Waste: The process is designed to optimize material usage, reducing scrap and improving overall efficiency.
Conclusion
Investment casting stands at the forefront of modern manufacturing, blending artistry and engineering to produce high-quality components. By understanding the detailed steps involved and the numerous advantages it offers, foundries can harness the power of investment casting to meet the demands of advanced industries, ensuring competitive advantage in an evolving market.